Dicyandiamide cured epoxy adhesives
I. Introduction
One of the most important parameters and starting points for the development of epoxy resin formulations is the epoxy resin curing mechanism and the selection of the specific curing agent to be used. Dicyandiamide is one of the most widely used catalysts for curing one-component epoxy adhesives. This type of adhesive has a long shelf life at room temperature, but offers relatively fast curing at temperatures above 150°C. Dicyandiamide cured epoxy adhesives have a wide range of uses, especially in the transportation, general assembly and electrical/electronic markets.
II. Dicyandiamide
Dicyandiamide (also known as “dicy”) is a solid latent curing agent that reacts with both the epoxy group and the secondary hydroxyl group. This curing agent is a white crystalline powder that is easily incorporated into epoxy formulations. Figure 1 is a graphical representation of the dicyandiamide molecule.
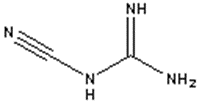
This curing agent cures through nitrogen-containing functional groups and consumes the epoxy and hydroxyl groups in the resin. The advantage of dicyandiamide is that it reacts with the epoxy resin only when heated to the activation temperature, and the reaction stops once the heat is removed. It is widely used in epoxy resins and has a long shelf life (up to 12 months). Longer shelf life can be obtained by refrigerated storage.
Due to its delayed cure (long shelf life) and excellent properties, dicyandiamide is used in many “Class B” film adhesives. Dicyandiamide is also one of the main catalysts for one-component, high-temperature curing epoxy adhesives.
In adhesive formulations, dicyandiamide is used in quantities of 5-7 pph for liquid epoxy resins and 3-4 pph for solid epoxy resins. it is generally dispersed with epoxy resins by ball milling. Dicyandiamide forms very stable mixtures with epoxy resins at room temperature because it is insoluble at low temperatures. The particle size and distribution of the epoxy-dicyandiamide system is critical for extending its shelf life. In general, the best performance is produced when the particle size of the dicyandiamide is less than 10 microns. Fumed silica is commonly used to keep the dicyandiamide particles suspended and evenly distributed in the epoxy resin. When formulated as a one-component adhesive system, epoxy dicyandiamide is stable when stored at room temperature for six months to one year. It is then cured by exposure to 145-160°C for approximately 30-60 minutes. Because of the relatively slow reaction rate at lower temperatures, the addition of 0.2% ~ 1.0% phenyl dimethylamine (BDMA) or other tertiary amine accelerators is sometimes used to reduce the cure time or lower the cure temperature. Other common accelerators are imidazole, substituted urea and modified aromatic amines. Substituted dicyandiamide derivatives can also be used as epoxy curing agents with higher solubility and lower activation temperatures. These techniques can reduce the activation temperature of epoxy-dicyandiamide mixtures to 125°C. Dicyandiamide-cured epoxy resins have good physical properties, heat and chemical resistance. Liquid epoxy cured with 6 pph dicyandiamide has a glass transition temperature of about 120°C, while high temperature curing with aliphatic amines will provide a glass transition temperature of no greater than 85°C.
III. One-component adhesive formulations
In one-component epoxy adhesives, the curing agent and resin are compounded together as a single material through an adhesive formulation. The curing agent system is selected so that it reacts with the resin only under appropriate processing conditions. Dicyandiamide-cured epoxy resins are very brittle. Through the use of toughening agents, such as terminated carboxybutyronitrile (CTBN), it is possible to formulate very elastic and tough adhesives without sacrificing the good properties inherent in unmodified systems. With toughened dicyandiamide-cured epoxies, peel strengths are approximately 30 lb/in and tensile shear strengths are in the range of 3000-4500 psi. Toughened dicyandiamide-cured epoxy adhesives also exhibit good resistance to heat cycling. The most effective accelerators for dicyandiamide systems are probably substituted ureas because of their synergistic effect on the performance of the adhesive and their exceptionally good latent delay. It has been shown that the addition of 10 pph of substituted urea to 10 pph of dicyandiamide will produce a bisphenol- a (DGEBA) epoxy liquid diglycidyl ester binder system that cures in only 90 min at 110 °C. However, this adhesive has a shelf life of three to six weeks at room temperature. If longer curing times are acceptable, curing can even be achieved at temperatures as low as 85°C.
Prev: What is the mechanism of action of polyacrylamide?
Next: Epoxy resin knowledge| Dielectric properties of epoxy resins